Increasingly, warehouses and the retail sector adopt perpetual inventory methods. A periodic system is only helpful if the business is small-scale and the inventory count is low, or if the employees are inexperienced in handling modern computers and networking technologies. The beginning inventory is added to the sales and closing inventory is deducted to reach the cost of goods sold. In a periodic system, no accounting is performed for the cost of goods sold until the end of the accounting period. The balance in the Merchandise Inventory account is then adjusted to the actual ending inventory, as determined by the physical count.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
You need enough inventory in stock to keep up with customer demand, but not so much that you are overpaying on storage costs. That’s why it’s crucial to have an inventory system in place, so you know exactly how much inventory you have at any given time. Perpetual inventory allows for more real-time inventory tracking, making it superior to other methods. However, the system requires consistent record-keeping and monitoring and is more expensive to set up than other methods.
Integration with Other Systems
Because you’re using a perpetual inventory system in this example, the recorded stock levels for this product are updated every time an order is fulfilled. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning introduces a new dimension to inventory management. These technologies can predict demand patterns by analyzing historical data and external factors. By anticipating future demand, businesses can better align inventory levels with customer needs, minimizing stockouts and excess inventory.
Inventory Valuation Methods
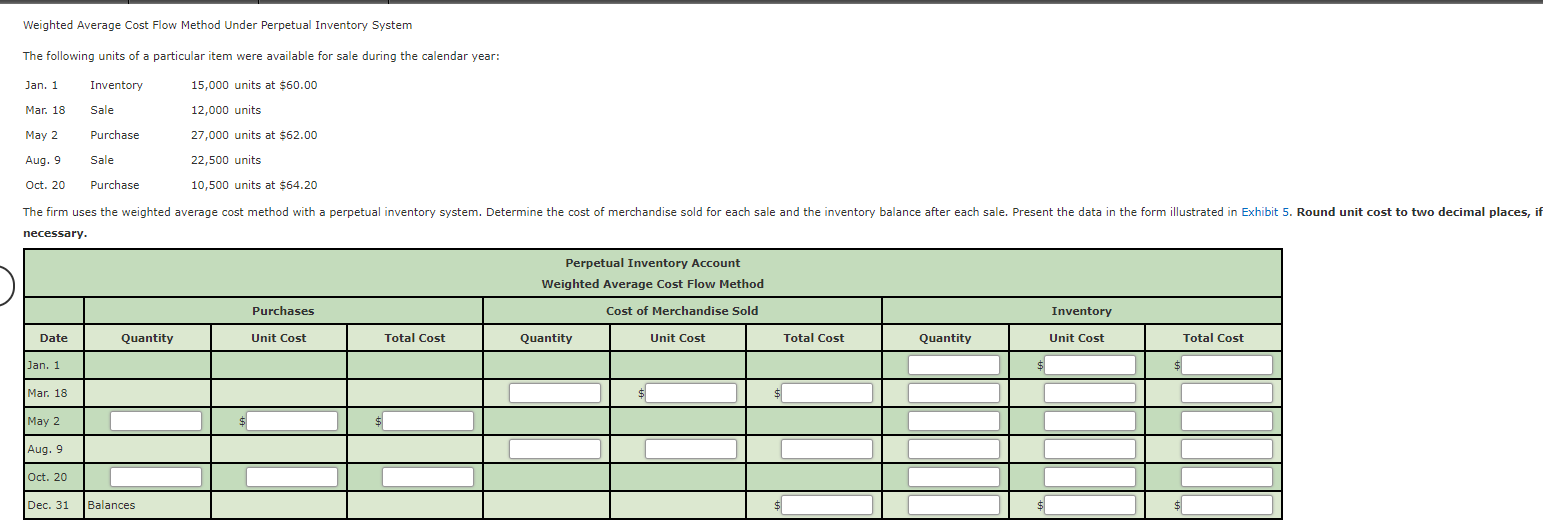
Under this method, the cost of goods sold (COGS) is calculated by dividing the cost of goods available for sale by the total number of units in inventory. It gives an average cost per unit, used to what is a balance sheet forecast value the COGS and ending inventory. A perpetual inventory system is a real-time computerized system that constantly monitors and updates inventory levels as goods are received, sold, or returned.
- When inventory arrives in your warehouse, the goods are received and immediately scanned into your inventory.
- The perpetual approach ensures immediate access to current inventory data, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Imagine owning an office supply store and trying to count and record every ballpoint pen in stock.
- The perpetual inventory system is more advanced and used more often than a periodic system.
Moreover, AI-driven systems can automate routine tasks, freeing up valuable time for employees to focus on strategic activities. By capturing data on each transaction, businesses can analyze patterns and trends, such as seasonal demand fluctuations or product popularity. This detail supports strategic planning and can lead to more efficient inventory management. For instance, a retailer might use this data to optimize stock levels, ensuring popular items are available while minimizing excess inventory of less popular products.
Systems
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) formula helps you decide when to purchase inventory and considers the cost of the goods against how much it costs to store them. The result dictates the optimal amount of stock to buy or manufacture to minimise expenses. The Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) formula considers the direct expenses of producing goods. These expenses include the cost of labour and materials and direct factory overhead costs, but not distribution or sales.
The accuracy of this balance is periodically assured by a physical count – usually once a year. If a difference is found between the balance in inventory account and the physical count, it is corrected by making a suitable journal entry (illustrated by journal entry number 6 given below). The common reasons of such difference include inaccurate record keeping, normal shrinkage, and shoplifting etc. Many companies counter this with periodic partial inventory counts, which provide a baseline for the perpetual system and are designed to provide a full physical inventory by the end of the period.

If you want to learn more about how to use these inventory methods, check out our guide on the different inventory valuation methods, with business examples. The stock accessible to clients for purchase and can be fulfilled is finished goods inventory. Sellers can determine inventory cost using the finished goods inventory formula.
The new purchase order is sent to your supplier, removing the need for manual ordering. The first record is a debit to accounts receivable with a matching credit to sales. As product businesses grow, the number of SKUs and complications typically grow too. At a certain point, manual inventory management becomes no longer feasible. Periodically compare your accounting books to on-hand inventory to ensure your inventory balances are correct. Some pros of perpetual inventory include its ability to provide up-to-date inventory information instantly, its easy access system, and how it reduces the requirement to count physical inventory.
Not only must an adjustment to Merchandise Inventory occur atthe end of a period, but closure of temporary merchandisingaccounts to prepare them for the next period is required. Temporaryaccounts requiring closure are Sales, Sales Discounts, SalesReturns and Allowances, and Cost of Goods Sold. Sales will closewith the temporary credit balance accounts to Income Summary. Visit Akounto’s blog for accounting knowledge and discover smart tips for running profitable, efficient, cost-effective business operations. Gross Profit is the difference between revenue earned from selling goods or services and the cost of producing or purchasing them for the accounting period. It means that the COGS is calculated based on the cost of the most recent inventory items, while the ending inventory is based on the cost of the oldest inventory items.