Despite its limitations, the scattergraph method can be a useful preliminary tool for understanding cost behavior, especially when combined with other methods for more rigorous analysis. All the data must be put into the graph, each point represents the number of units produces and the total cost spend. And there you have it—the High-Low Method demystified, sans the usual jargon. Now, armed with this knowledge, you can confidently tackle your mixed costs and impress your colleagues at the next budget meeting. And there you have it—the unvarnished truth about mixed costs, sans Google searches or secret scrolls.
Related AccountingTools Courses
- The line intersects the data point for March ($480,000 production costs; 330 units produced).
- A problem arises when a cost contain features of both fixed and variable costs.
- The total variable is calculated by subtracting fixed costs from the total mixed cost.
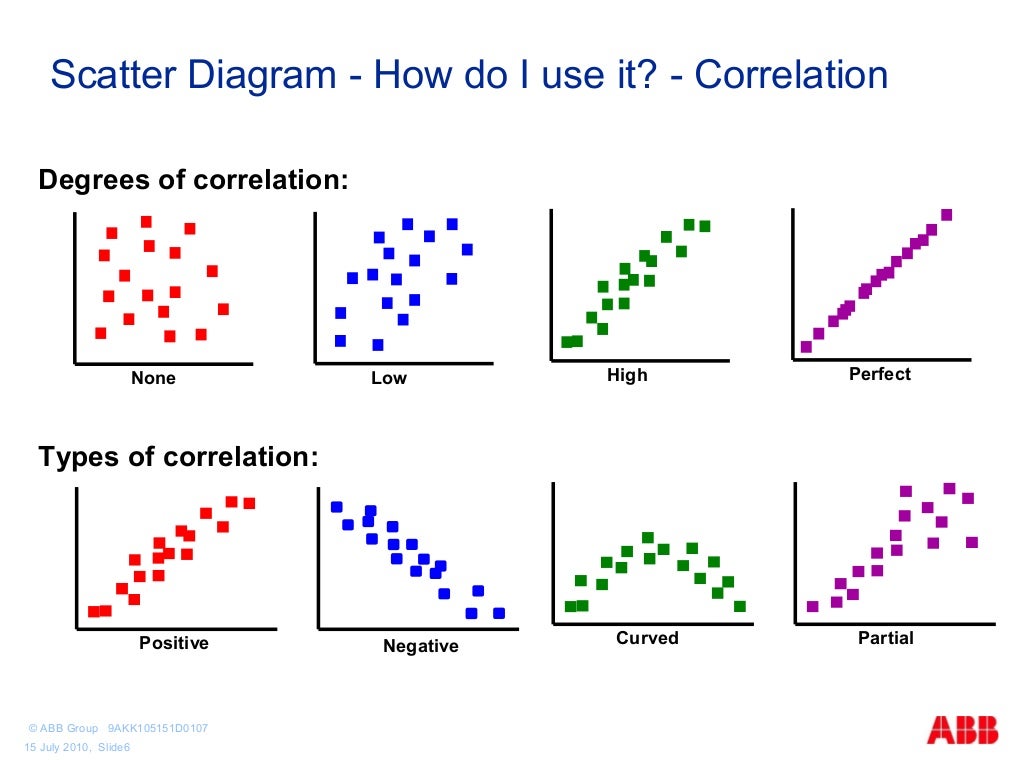
- The method derives its name from the overall image of the graph, which consists of many scattered dots.
- Utilities often serve as a prime example of mixed costs, where a base charge remains constant, but additional usage leads to higher costs.
- Notice that the line hits the data point for July (3,500 units produced and $230,000 total cost).
Costs that vary directly with changes in the level of activity or volume within an organization. The way in which a cost changes in relation to changes in the level of activity or volume within an organization. Understanding how to effectively use the scattergraph method can significantly enhance the accuracy of cost predictions and budgeting processes. Costs that remain constant, regardless of changes in the level of activity or volume within an organization. In March, Waymaker produced 1,000 units and used 2,000 hours of production labor.
Fixed Costs and Variable Costs
With this method, the mixed cost is separated into a fixed and variable costs. Scatter graph method is a visual representation used to divide fixed and variable cost components from a mixed cost figure. This is done by plotting the points at which the cost on one axis and activity on another axis meet to find out the correlation between these two variable.
Scatter Graph Method: Cost Segregation
Susan did request that her staff prepare a scattergraph and review it for any unusual data points before performing regression analysis. Based on the scattergraph prepared, all agreed that the data was relatively uniform and no outlying data points were identified. Once the scattergraph is constructed, the next step is to interpret the plotted data to distinguish between fixed and variable costs.
Interpreting the results of a scattergraph involves more than just identifying fixed and variable costs; it requires a deeper analysis to uncover insights that can drive strategic decisions. One of the first aspects to consider is the overall pattern of the data points. A well-defined trend line suggests a strong correlation between costs and activity levels, which can be useful for predicting future costs.
Costs and Scatter Graphs
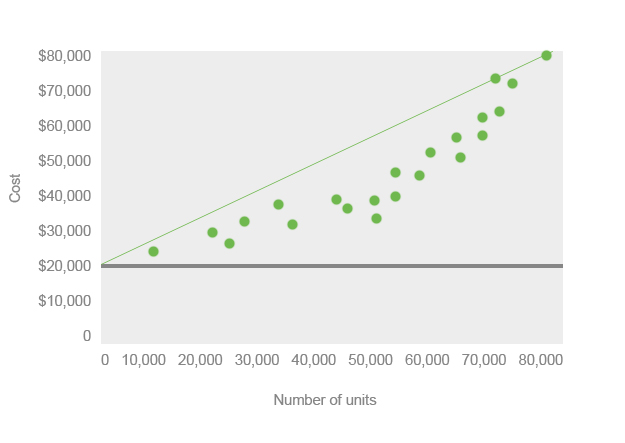
No matter the production level, there’s a consistent cost of $500 (fixed cost). Suppose a small manufacturing company wants to understand the relationship between the number of units produced and the total production cost, which includes both variable and fixed costs. It is also important to consider the presence of mixed costs, which contain both fixed and variable components.
By calculating the slope, one can determine the variable cost rate, which is essential for budgeting and forecasting purposes. The method derives its name from the overall image of the graph, which consists of many scattered dots. 5 hidden ways to boost your tax refund Ideally, the result of a scattergraph analysis is a formula with the total amount of fixed cost and the variable cost per unit of activity. The scatter-graph method is a graphical approach in calculating fixed and variable costs.
Therefore, it is advisable to use a reliable accounting software like QuickBooks or Xero, which can streamline the data collection process and ensure that all necessary information is captured accurately. Data are plotted as points on the graph, and a regression line that runs through the dots represents the best fit of the relationship between the variables. Have you noticed that your electricity bill fluctuates with the different seasons?